Mono vs Bipolar Cautery
Mono vs Bipolar Cautery
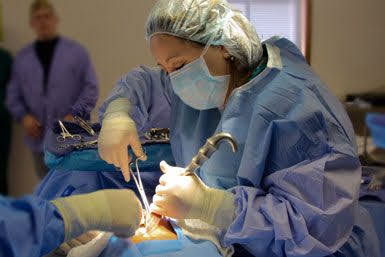
Cautery may be a therapeutic method utilized to evacuate or crush undesirable tissue or control bleeding by applying heat to the affected area. The initial incision is made by a scalpel. The Electrosurgical unit (ESU) is not used to incise the skin. Electrosurgery can be used on fat, fascia, muscle, internal organs, and vessels. ESUs operate at frequencies between 100,000 and 10,000,000 Hz. This current can be passed through tissue without causing stimulation of muscles or nerves.
Electrosurgery differs from electrocautery. Electrocautery is the use of a unidirectional current generated by a self-contained battery-operated disposable instrument with a wire at the tip. The wire heats when activated and coagulates the tissue. The energy does not enter the patient’s body. The ESU uses an alternating current that passes through the patient’s tissues and returns to the generator.
Two forms of cautery are commonly used in surgery:
Each type has specific uses and considerations.
Monopolar and bipolar cautery are two distinctive methods utilized to perform this procedure.
In monopolar cautery, an electrical current is passed through a single anode, which is put on the influenced tissue. The current streams through the tissue to a establishing cushion put on another portion of the patient's body, completing the circuit. The warm produced by the current crushes the undesirable tissue or cauterizes the dying vessel.
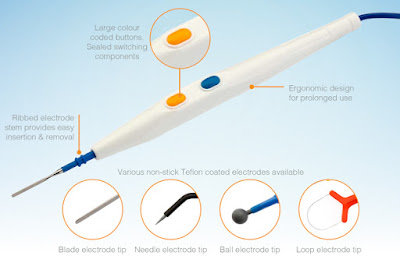
On the other hand, bipolar cautery uses two electrodes that are placed directly on the tissue being treated. The electrical current flows only between these two electrodes, creating heat that cauterizes the tissue or stops the bleeding.
- The main difference between the two techniques is that in monopolar cautery , the electrical current flows through the patient's body, whereas in bipolar cautery, it is limited to the immediate area being treated. Monopolar cautery is typically used for larger surgical procedures, while bipolar cautery is more commonly used for smaller, more delicate procedures.
- Another difference is that monopolar cautery may cause electrical interference with other medical devices or with the patient's heart rhythm, while bipolar cautery is less likely to do so.
Overall, both monopolar and bipolar cautery are effective techniques for removing tissue or controlling bleeding, and the choice of which technique to use depends on the specific situation and the preferences of the surgeon.
Bipolar Cautery offers several advantages over monopolar :
- Reduced risk of electrical interference: Since the electrical current used in bipolar is limited to the immediate area being treated, there is less risk of electrical interference with other medical devices or the patient's heart rhythm.
- Precision: Bipolar cautery is more precise than monopolar cautery, making it better suited for delicate procedures that require greater accuracy.
- Reduced tissue damage: Bipolar cautery produces less tissue damage than monopolar cautery since the electrical current is limited to the immediate area being treated.
- Reduced smoke and odor: Bipolar cautery produces less smoke and odor compared to monopolar cautery, which can be beneficial for both the surgeon and the patient.
- Shorter recovery time: Since bipolar cautery causes less tissue damage and trauma, it can result in a shorter recovery time for the patient.
Safety Factor for the Use of Cautery
A safety factor that can be employed is to follow established protocols and guidelines for cautery use. These guidelines typically include the following:
Proper training and certification: Only trained and certified healthcare professionals should be allowed to use cautery devices. This includes understanding the appropriate use of the device, as well as the risks and potential complications associated with its use.
Preoperative evaluation: Prior to the use of cautery, the patient should undergo a thorough preoperative evaluation to identify any factors that may increase the risk of complications.
Use of appropriate equipment: The appropriate cautery device should be selected based on the type of procedure being performed, the tissue being treated, and other factors.
Proper use of grounding pads: Grounding pads should be applied to the patient to prevent the risk of electrical burns.
Monitoring during and after the procedure: The patient should be continuously monitored during the procedure and closely observed for any signs of complications after the procedure.
By following these guidelines, healthcare professionals can help to minimize the risks associated with the use of cautery and improve patient safety.