How hand washing and scrubbing differentiate?
Hand washing :
- Purpose: Primarily aimed at removing dirt, bacteria, and viruses from the hands to prevent the spread of infection.
- Technique:
- Duration: Typically lasts about 20 seconds.
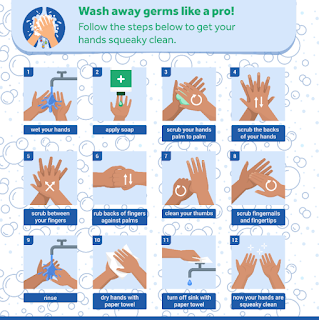
- Method: Involves wetting the hands with water, applying soap, and thoroughly rubbing all surfaces of the hands (including between fingers and under nails).
- Rinsing: Hands are rinsed under running water, and then dried with a clean towel or air dryer.
- Context: Commonly practiced in everyday situations (e.g., before eating, after using the restroom).
Surgical Scrubbing
- Purpose: Aimed at reducing the microbial load on the hands and forearms before surgical procedures to minimize the risk of surgical site infections.
- Technique:
- Duration: Typically lasts 5 to 10 minutes, depending on protocols.
- Method: Involves a thorough scrubbing of the hands and forearms with a designated surgical scrub solution (often containing antiseptics like chlorhexidine or povidone-iodine).
- Scrubbing: Uses a specific technique that includes:
- Scrubbing each finger, hand, and forearm systematically.
- Often using a brush to enhance friction and remove debris.
- Rinsing: Hands are rinsed under running water, ensuring that water runs from the cleanest (hands) to the least clean (arms) areas.
- Context: Performed by surgical team members in preparation for sterile procedures.
Steps for the Brush and Stroke Method:
- Gather Supplies: You will need an antimicrobial soap, a sterile brush or sponge (with bristles on one side), and sterile water.
- Initial Hand Rinse: Wet your hands and forearms thoroughly under warm running water.
- Apply Antimicrobial Soap: Dispense a generous amount of antimicrobial soap onto your hands and forearms.
- Scrub Fingernails and Cuticles:
- Use the bristled side of the brush to clean under your nails and around your cuticles
- Stroke each nail 30 times (recommended in surgical settings) in a downward motion.
- Rinse the brush intermittently in sterile water to remove debris.
- Scrub Each Finger:
- Start with the fingertips and scrub each finger individually, focusing on the spaces between fingers. Use 10–20 strokes for each side of the finger.
- Repeat this process for each finger on both hands.
- Scrub the Palms and Back of the Hands:
- Use the sponge side of the brush to scrub the palms in a circular motion.
- Scrub the back of the hands using a similar stroke pattern, paying extra attention to the knuckles and other folds of the skin.
- Scrub the Wrists and Forearms:
- Move up to the wrists and scrub in circular strokes.
- Gradually scrub up to the elbows in circular motions, using long, sweeping strokes, especially in surgical settings.
- Cleaning of the entire forearm.
- Rinse Thoroughly: Rinse your hands and forearms under sterile running water, keeping your hands higher than your elbows to avoid water running from the elbows back to the hands.
- Dry Hands: After scrubbing, dry your hands and forearms with a sterile towel, again ensuring your hands remain elevated above your elbows.
Preparation before hand hygiene :
• The skin and nails should be kept clean.
• A non oil based product is recommended to protect the skin.
• Fingernails should not reach beyond the fingertips to avoid glove puncture.
• Fingernail polish should not be chipped or cracked.
• All jewelry is removed from the fingers, wrists and neck .
• All hair should be covered by head wear .
• Adjust the disposable mask snugly and comfortably over the nose and mouth.
Comfortable water temperature is used as hot water increases chafing and cooler water helps to minimize dry skin.