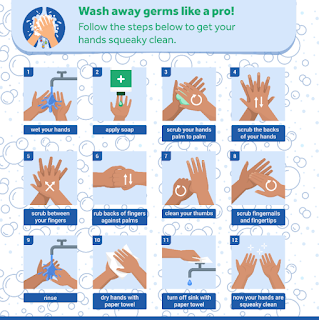
Tips to prevent fogging on glasses when wearing a mask

Tips to prevent fogging on glasses when wearing a mask Here are some tips to prevent fogging on glasses when wearing a mask: The standard technique of tying a surgical mask involves knotting the two ties so they lie above and below the ear in a near parallel appearance ( Fig 1 ). Our method consists of knotting the superior tie first with it lying directly below the ear. The inferior tie is brought up in front of the ear and knotted over the crown of the head ( Fig 2 ). Clean your glasses with soap and water before putting on your mask. Adjust your mask to fit securely and tight on your face. Create a seal around your nose by pressing down on the top of the mask Breathe out slowly and calmly. Try using a mask with a moldable nose bridge or insert a small piece of tissue under the top of the mask. Wear glasses with anti-fog coating. Tying a surgical mask to prevent fogging Authors: DJ Jordan and R Pritchard-JonesAUTHORS INFO & AFFILIATIONS


.jpeg)